The Location Engine - Key Concepts
Table of Contents
Digital Matter provides its Device Manager Device Management platform as a web-based platform solution for partners to manage devices over-the-air (OTA).
Digital Matter has developed the Location Engine (LE) as a module of Device Manager to perform server-side processing of device data for devices that use alternative low-power techniques, like the ‘Edge’ based devices. This technology allows the devices to operate at extremely low power levels. In short, the 'low power techniques' typically mean that the device quickly scans for GNSS (GPS), Wi-Fi and cell tower information, and rather than computing this on the device - the raw data is sent, to be resolved by the Location Engine.
The services included with Location Engine cover:
- Resolving GNSS scan data to locations
- Location lookups using WiFi location data
- Location lookups using cell tower data (if applicable)
- LoRa Edge device management (if applicable)
- LoRa gateway triangulation (if applicable)
- Sending GNSS almanac data, and current position down to the device to ensure the GNSS performs well
- Other data enrichment processes
- The configuration and management of the processes, including which filtering options, and which location services to use
- All the other benefits of Device Manager platform - see the Welcome To Device Manager for details.
Concepts
Cellular Devices
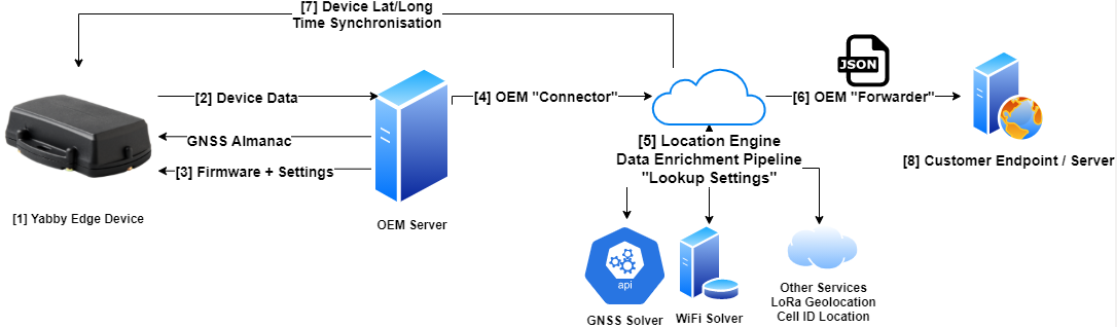
Overview:
- The 'Edge' device scans for GNSS, Wi-Fi and cell signals.
How this is handled can be configured, see - Yabby Edge Cellular - Location Scanning Parameters - Devices send this 'raw' GNSS, WiFi and Cell ID data to Device Manager
- Device Manager manages device firmware, settings, debugging and more
- A 'connector' must be set on the device to then pass the the data to the Location Engine
- Data enrichment is performed. The device resolves the location via a variety of services. To compute the lat/long from the raw data. The "Lookup Settings" can be configured via the Device Manager. These settings determine which services to use and other options
- A "Forwarder" defines where the enriched data (with solved position) must go.
- The Location Engine also performs several other important functions that ensure device performance including sending down GNSS Almanac data and an estimated position to the device.
- The customer endpoint receives the location data in JSON format.
The Location Engine (LE) is a robust Cloud solution that comprises queues and scalable virtual functions to ensure that messages are processed in order and delivered to the defined Endpoint Server.
LoRaWAN Devices
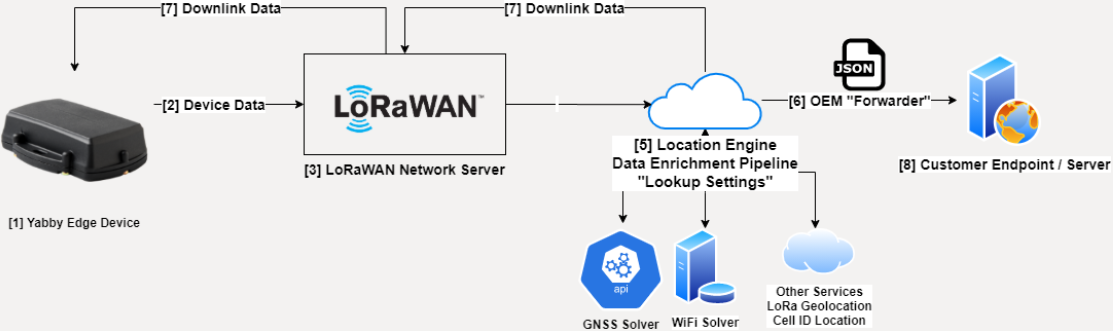
Overview:
The general architecture is similar to the Cellular example. However devices send data to the Location Engine via a LoRaWAN network server, rather than Device Manager. Currently supported LoRaWAN network servers are:
- TTN
- Actility
- Senet
- ChirpStack
- Everynet
- LoRIoT
- Helium
See this folder for details.
The process in [7] supports sending Almanac Data, a position estimate, performing time synchronisation and updating parameters via downlink. The Location Engine must instruct the network server to send this information to the device.
Device Connectors [Cellular Only]
Device 'connectors' are a concept in Device Manager which apply to all devices in the Digital Matter range. For 'traditional' devices, the user would configure a connector to send the raw device data (which has location data) through to their endpoint.
For 'Edge' devices, the setup is quite similar. However we must configure the connector to send data to the Location Engine for processing, and the Location Engine Forwards the data to the customer endpoint.
Lookup Settings
In the general/default case for the Edge devices, data enrichment is performed in the order of best accuracy and typically will follow the process of:
- GNSS Location Solving
- WiFi lookup solving
- Fallback to cell tower location or LoRa gateway location (where applicable)
The LE has the capability to filter lookup results according to the required accuracy of the enrichment step's result.
The LE uses the first successful location within accuracy parameters specified.
The steps to perform as well as the parameters to filter results depend on the use case.
Partners are encouraged to contact our support team if devices are not performing as expected - as we can assist in tweaking settings for the optimum performance.
Forwarder
A Forwarder is configured on the Forwarder tab in the Device Manager Server UI. It defines the endpoint LE data is forwarded to.
Configure LE Data to be sent to your endpoint (Cellular Devices)
See the Guide here for cellular devices - Send Edge Device Data to my Endpoint (Cellular)
API Credentials [LoRaWAN Only]
To handle almanac file downloads, and sending a position estimate to the device (required for proper GNSS performance) - the LE must send this information down to the device. It does this via the LoRaWAN network server, and to allow for the LE to send downlinks via the Network server, API credentials must be configured via the Device Manager UI.
See Setting up a Yabby Edge LoRaWAN Device via TTN (v3) for an example of this process.
Configure LE data to be sent to your endpoint (LoRaWAN)
Configuration steps are slightly different based on the specific LoRaWAN network server. See the guides available here
Pricing
Different use cases require different position reporting rates from devices, and LE is designed to accommodate this with a flexible pricing model. Contact your sales representative for more details.
